
What is Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has emerged as a transformative technology that has reshaped the way businesses and individuals store, access, and manage data. At its core, cloud computing allows users to access and utilize computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. This introductory article will delve into the definition of cloud computing, explore its various service models (Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service), and examine its deployment models (public, private, and hybrid clouds). We will also highlight the key benefits of cloud computing, such as cost efficiency, scalability, and accessibility, while addressing the challenges and considerations it presents. Through this exploration, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of cloud computing and its significant impact on the digital landscape.

What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer flexible resources, faster innovation, and economies of scale. It allows users to access and use computing power and data storage without having to own or manage physical servers, with services provided on an as-needed basis.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- On-demand self-service: Users can automatically provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
- Broad network access: Services are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, laptops, and PDAs).
- Resource pooling: The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand. There is a sense of location independence in that the customer generally has no control or knowledge over the exact location of the provided resources but may be able to specify location at a higher level of abstraction (e.g., country, state, or datacenter).
- Rapid elasticity: Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released, in some cases automatically, to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand. To the user, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be appropriated in any quantity at any time.
- Measured service: Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts). Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for both the provider and consumer of the utilized service.
Service Models
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Example providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Compute Engine.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers hardware and software tools over the internet, typically for application development. Examples include Google App Engine, Heroku, and Microsoft Azure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, on a subscription basis. Examples include Google Workspace, Salesforce, and Microsoft Office 365.
Deployment Models:
- Public Cloud: Services are delivered over the public internet and are available to anyone willing to pay for them. Examples include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Private Cloud: The cloud infrastructure is exclusively used by a single organization. It can be managed internally or by a third party and hosted either internally or externally.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This provides businesses with more flexibility and more deployment options.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the IT industry by providing scalable, efficient, and cost-effective solutions, enabling businesses and individuals to leverage powerful computing resources and innovative technologies without substantial upfront investments in physical hardware or ongoing maintenance and upgrades.
Progression of cloud Computing
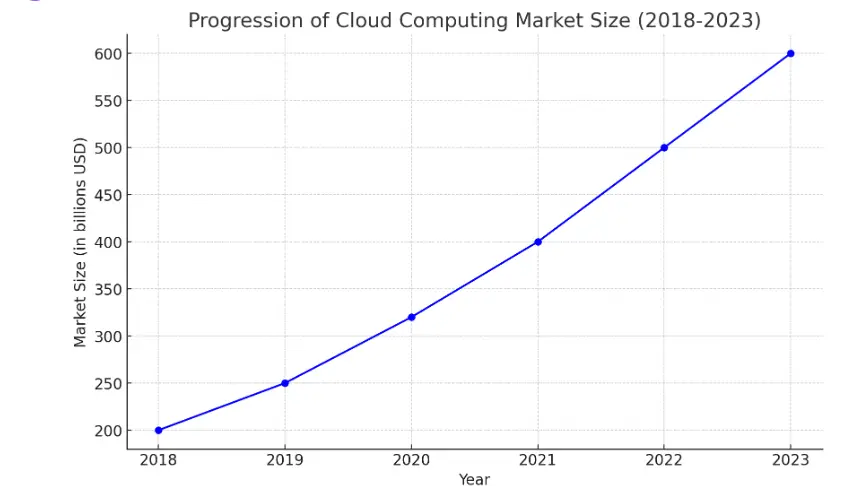
The graph above illustrates the fictional progression of the cloud computing market size from 2018 to 2023, showcasing a steady increase in market value over the years. This visual representation highlights the significant growth and adoption of cloud computing technologies across various industries, reflecting the increasing reliance on cloud services for digital transformation, innovation, and efficiency.
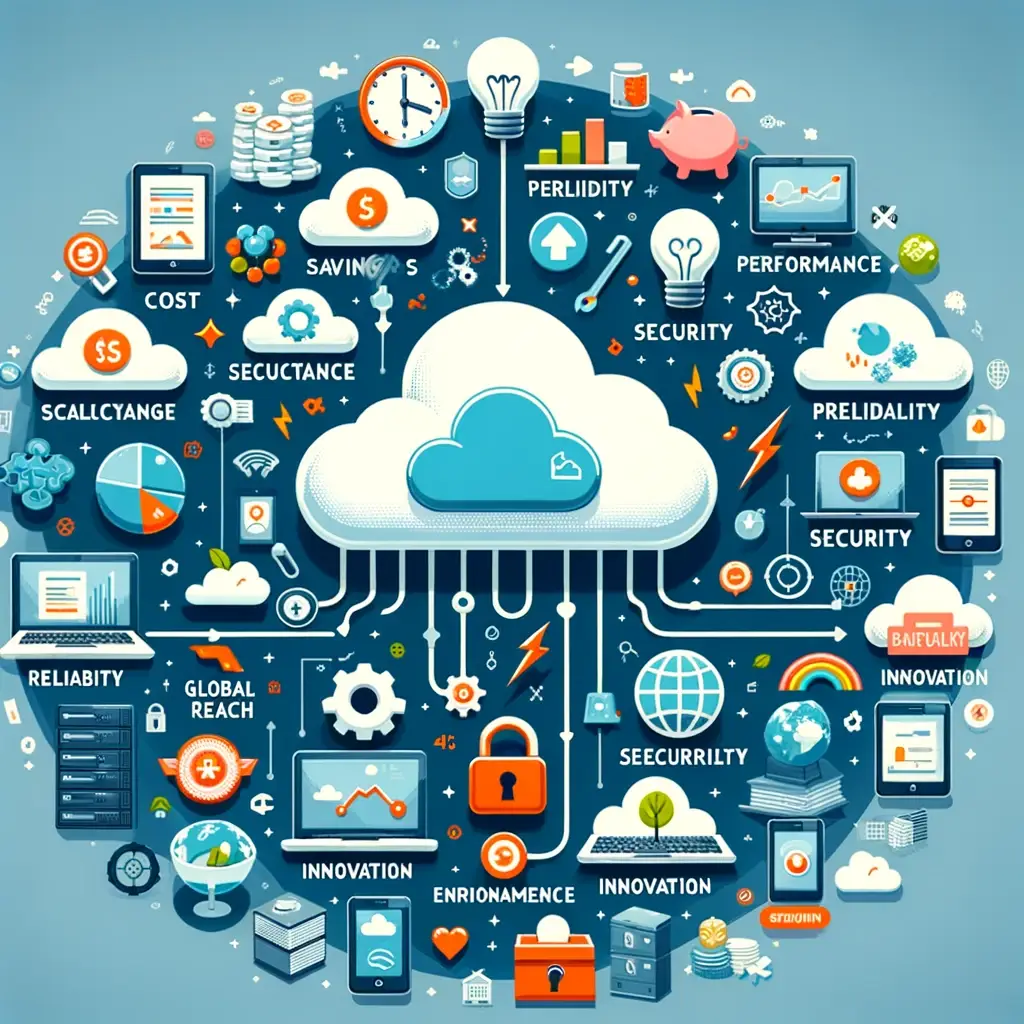

The benifits of cloud computing
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits to businesses and individuals, making it a popular choice for managing computing resources and services. Here are some of the key advantages:
Cost Efficiency: Reduces the cost of purchasing hardware and software, setting up and running on-site datacenters, the electricity for power and cooling, and IT experts for managing the infrastructure. It follows a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you pay only for what you use.
Scalability: Offers the ability to scale computing resources up or down easily, depending on demand, without the need for significant upfront investment. This elasticity is ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
Performance: The major cloud services run on a worldwide network of secure datacenters, which are regularly upgraded to the latest generation of fast and efficient computing hardware. This offers several benefits over a single corporate datacenter, including reduced network latency for applications and greater economies of scale.
Speed and Agility: Resources can be provisioned in minutes, giving businesses a lot of flexibility and taking the pressure off capacity planning. This enables faster development and deployment of applications.
Productivity: On-site datacenters typically require a lot of “racking and stacking”—hardware set up, software patching, and other time-consuming IT management chores. Cloud computing removes the need for many of these tasks, so IT teams can spend time on achieving more important business goals.
Reliability: Cloud computing makes data backup, disaster recovery, and business continuity easier and less expensive because data can be mirrored at multiple redundant sites on the cloud provider’s network.
Security: Many cloud providers offer a set of policies, technologies, and controls that strengthen your security posture overall, helping protect data, apps, and infrastructure from potential threats.
Global Scale: The ability to scale your services to millions of users globally at a moment’s notice. Cloud computing provides the flexibility to expand to different regions and markets easily, without the need to establish a physical presence.
Innovation: With the cloud, businesses can take advantage of the latest technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) more easily. This can help to drive innovation, improve customer experiences, and streamline operations.
Environmentally Friendly: By utilizing cloud resources, businesses can ensure they’re using only the energy they need, which can reduce their carbon footprint. Cloud data centers often have better resource utilization rates than traditional data centers, making them more environmentally friendly.
These benefits demonstrate why cloud computing has become a fundamental part of the IT strategy for businesses of all sizes.

Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud computing represents a significant shift in how technology is consumed and managed, offering a flexible, efficient, and scalable solution that can accommodate the needs of businesses and individuals alike. Its ability to provide on-demand access to computing resources, without the need for significant upfront investment in physical infrastructure, has democratized access to technology. By enabling cost savings, enhancing performance, and promoting innovation, cloud computing has become a cornerstone of the digital transformation era.
The scalability and flexibility offered by cloud services mean that organizations can adapt more quickly to market changes and customer demands, without the burden of over-provisioning resources. The move towards cloud computing also reflects a broader trend towards sustainability, as it promotes more efficient use of energy and resources.
Moreover, the security and reliability improvements provided by cloud platforms are crucial for ensuring the integrity and availability of data, which is increasingly important in a world where data breaches and cyber threats are common.
As we look to the future, the continued evolution of cloud computing technologies, including advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things, will further expand its capabilities and applications. This evolution will not only enhance business processes and efficiencies but also open new avenues for innovation and growth.
Ultimately, cloud computing is not just a technology trend; it is a fundamental change in the IT landscape that is enabling organizations to focus more on their core business activities while leveraging the latest in technology advancements. Its impact on business efficiency, cost reduction, and innovation is profound, making it an essential component of modern business strategy.


